JOrange-C
| Commercial name | JOrange-C |
| Application | Skin care |
| Function | Smoothing / Lifting effect |
| Use level | 1-3% |
Benefits
Formulated with α hydroxy acids and active ingredients of natural origin, JOrange-C restores elasticity, brightness, and provides an immediate cosmetic “lifting effect” to the skin on the face.
Recommended Applications
- Shampoo
- Hair Masks
- Prodotti styling
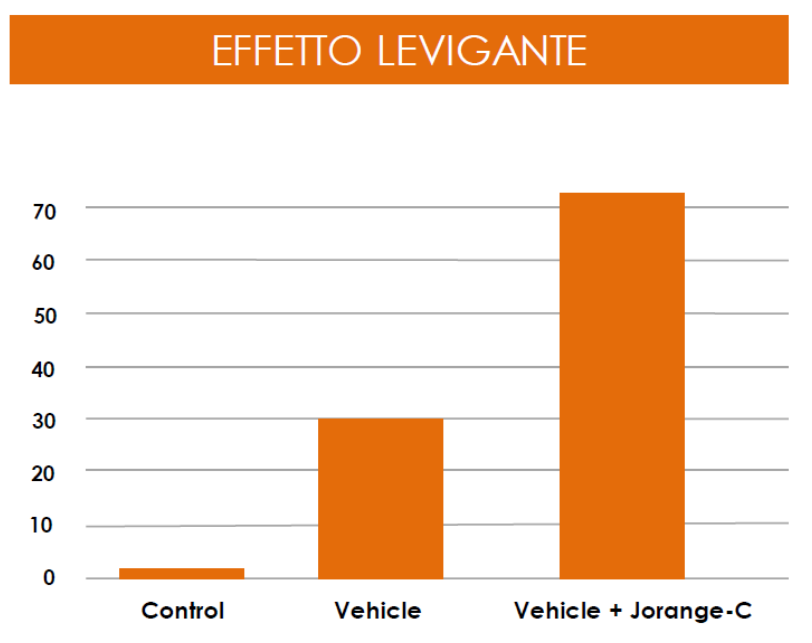
EFFICACY TEST
The effectiveness of JOrange-C was tested on reconstructed human epidermis in vitro. The 3D skin models were topically treated with a vehicle formulation containing 3% JOrange-C and with an unmodified vehicle formulation.
The data obtained showed a greater exfoliating effect from the JOrange-C-containing vehicle (Graph 1).
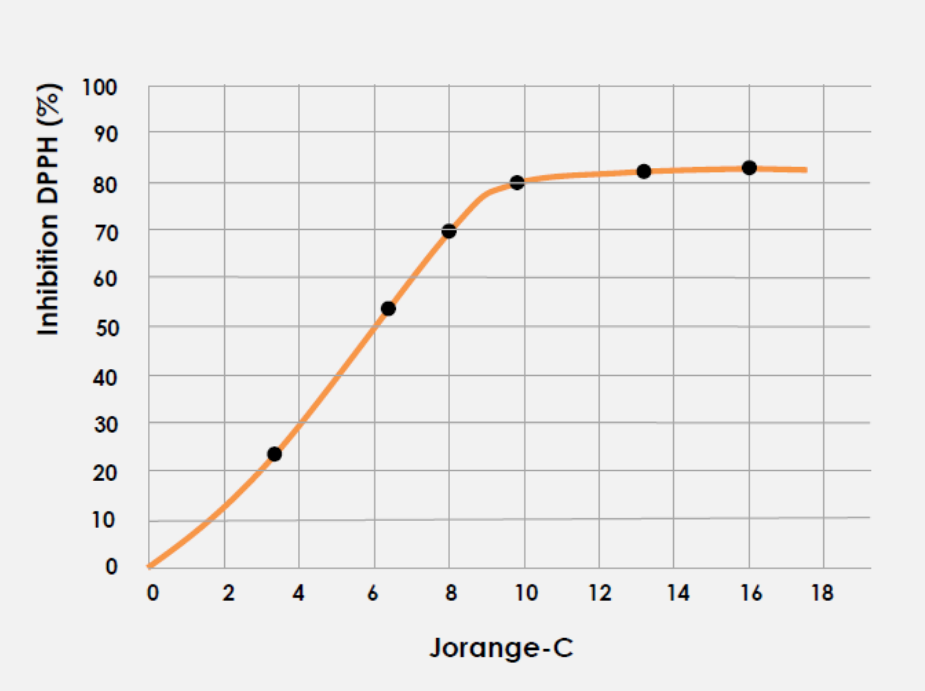
EVALUATION OF ANTIOXIDANT ACTIVITY: DPPH FREE RADICAL SCAVENGING ACTION
DPPH (2.2′ diphenyl.-1 picrylhydrazyl) is an organic free radical with a peak absorption at 515-528 nm and allows to evaluate the antioxidant activity of various compounds.
The reaction involves the reduction of the radical DPPH, by the antioxidant molecule, to give a compound of yellow color, the diphenylpicrilidrazine.
The extent of the reduction reaction depends on the molecule’s ability to act as an electron donor
The effectiveness shown in inhibiting the DPPH radical was shown in Figure 2.
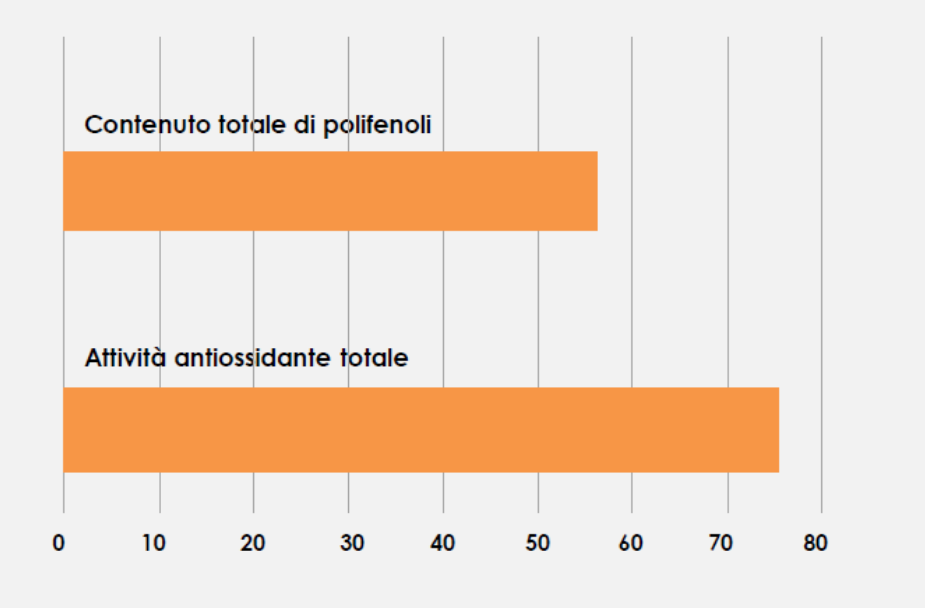
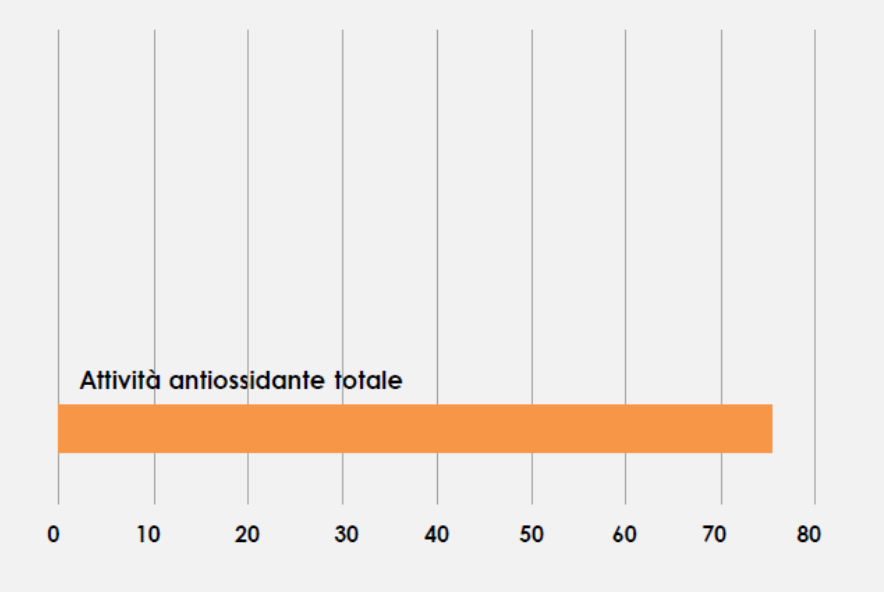
DETERMINATION OF TOTAL ANTIOXIDANT ACTIVITY
Total antioxidant activity was determined using the Molybdate test, which is based on a redox reaction where antioxidant fractions in the sample facilitate the reduction of Mo (VI) to Mo (V), forming a green phosphate/Mo (V) complex at acidic pH, with a maximum absorption peak at 695 nm.
Total antioxidant activity was expressed as mg ferulic acid equivalents per gram of JOrange-C (mg eq FA/g) (Graph 3)
TOTAL POLYPHENOL CONTENT
The total polyphenol content was determined using the Folin-Ciocalteu assay. Phenolic compounds undergo a complex redox reaction with phosphotungstic and phosphomolybdic acids present in the Folin-Ciocalteu reagent. The development of color is due to electron transfer, resulting in the formation of chromogens where metals have a lower valence.
The content of available phenolic groups was expressed as milligrams equivalent of catechin per gram of JOrange-C (mg eq CA/g) (Graph 4).