AntioxCA
| Commercial name | ANTIOX-CA |
| Application | Skin Care |
| Function | Antioxidant |
| Use level | 1-3% |
Directions for use:
Formulated with active ingredients of natural origin, Antiox-CA, a complex of antioxidant actives, works to minimize the production of free radicals, responsible for premature skin aging, and promotes cellular renewal.
Recommended applications:
- Shampoo
- Anti-aging products
- Antioxidant products
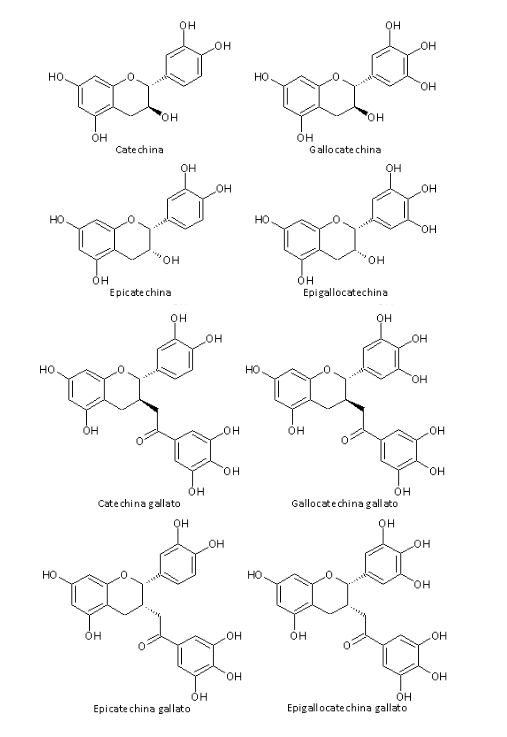
Green tea (Camellia sinensis) belongs to the Theaceae family. Well-known for its antioxidant action, it is useful in countering cellular aging. The extract mainly consists of polyphenols and xanthine bases (theophylline).
The polyphenols, predominantly catechins (Fig. 1), are responsible for the pronounced antioxidant properties of the phyto-complex, which translates into a protective action at the microcirculation level and free radical scavenging in anti-aging products. Moreover, thanks to the presence of tannins, green tea extract possesses dermopurifying and astringent properties, useful in the treatment of oily and impure skin.
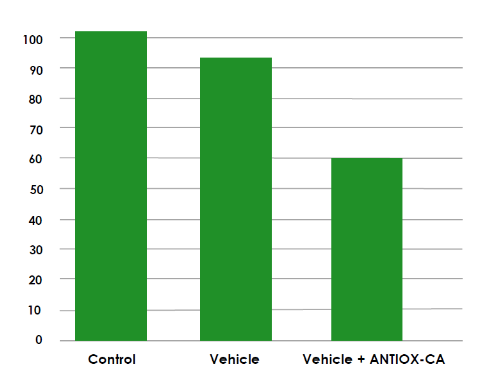
DETERMINATION OF ANTI-POLLUTION EFFECT
The production of intracellular ROS (Reactive Oxygen Species) was determined using DCF-DA (2′7′-dichlorofluorescein diacetate) and a culture of human keratinocytes HaCaT exposed to a pollutant agent, namely Benzopyrene, a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon that induces upregulation of cytochrome P 450 by activating the Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor (AhR), causing inflammation and cellular aging. The cells were treated with a vehicle formulation containing 3% of ANTIOX-CA and with an unmodified vehicle formulation (Graph 1).
The data obtained show that ANTIOX-CA allowed a reduction in the percentage of intracellular ROS produced following treatment with benzopyrene.
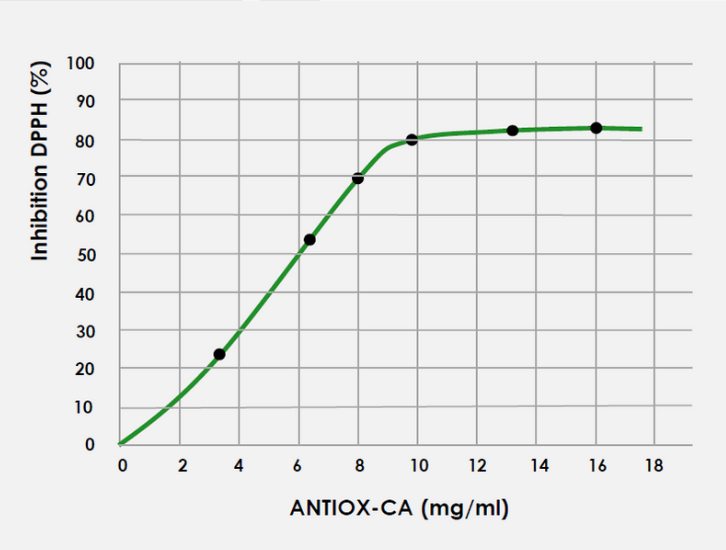
EVALUATION OF ANTIOXIDANT ACTIVITY: DPPH FREE RADICAL SCAVENGING ACTION
DPPH (2,2′-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl) is an organic free radical with a maximum absorption peak at 515-528 nm, allowing the assessment of antioxidant activity of various compounds through a spectrophotometric measurement.
The scavenging activity against DPPH radicals was expressed as a percentage of inhibition (Graph 2).
DETERMINATION OF TOTAL ANTIOXIDANT ACTIVITY
Total antioxidant activity was determined using the Molybdate test, which is based on a redox reaction where antioxidant fractions in the sample facilitate the reduction of Mo (VI) to Mo (V), forming a green phosphate/Mo (V) complex at acidic pH, with a maximum absorption peak at 695 nm.
The total antioxidant activity was expressed as milligrams equivalent of ferulic acid per gram of ANTIOX-CA (mg eq FA/g) (Graph 3).
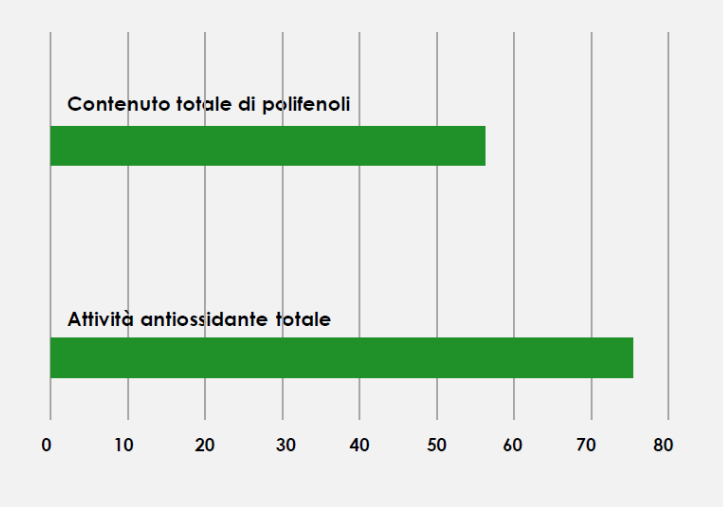
DETERMINATION OF TOTAL POLYPHENOL CONTENT
The total polyphenol content was determined using the Folin-Ciocalteu assay. Phenolic compounds undergo a complex redox reaction with phosphotungstic and phosphomolybdic acids present in the Folin-Ciocalteu reagent. The development of color is due to electron transfer, resulting in the formation of chromogens where metals have a lower valence. The content of available phenolic groups was expressed as grams equivalent of catechin per gram of ANTIOX-CA (mg eq CA/g) (Graph 3).
