Active-CO
| Commercial name | Active-CO |
| Application | Hair Care |
| Function | Hair Loss Control |
Suggested Applications:
- Leave-on Anti-Hair Loss Treatment
- Shampoo
- Conditioner
Efficacy Assessment
5α-REDUCTASE INHIBITION
The conversion of testosterone to the more active compound dihydrotestosterone (DHT) is mediated by the activity of 5α-reductase (5AR). DHT is responsible for the miniaturization of hair follicles, leading to irreversible hair loss. Inhibition of this enzyme represents an effective strategy in managing androgenetic alopecia (AGA).
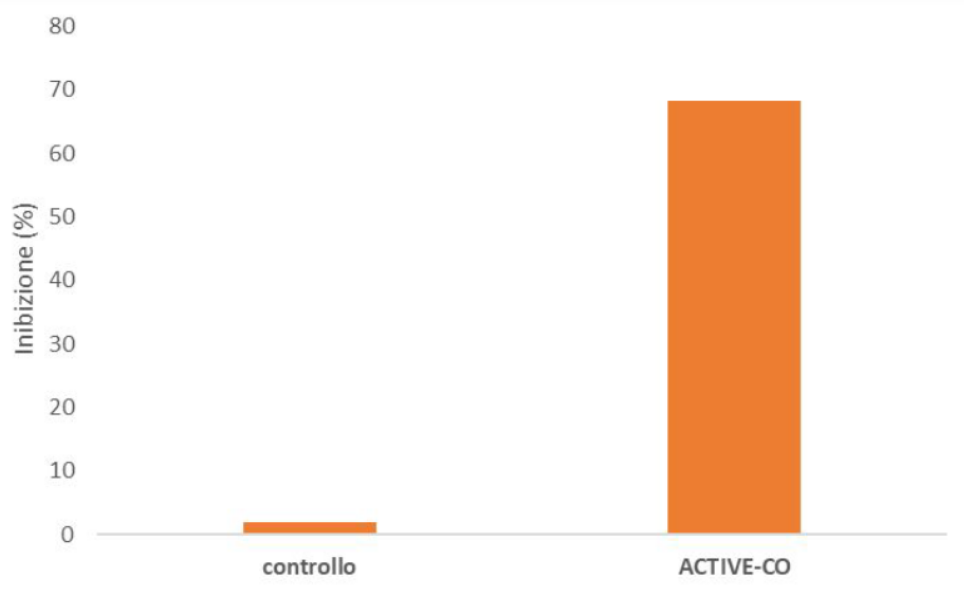
To evaluate the ability of ACTIVE-CO to inhibit 5AR enzyme activity, an homogenate from LNCaP cells (Androgen-dependent prostate cancer cells) was used as the enzyme source.
The results obtained showed an inhibition percentage of 68.3 ± 0.7%.
NITRIC OXIDE SCAVENGING ACTIVITY – ANTI-INFLAMMATORY ACTION
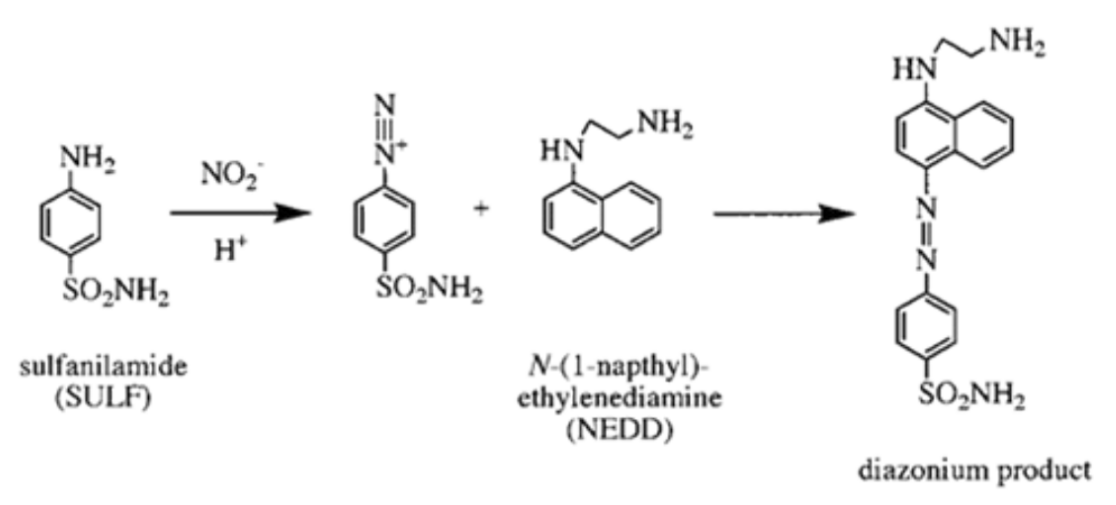
The in vitro determination of nitric oxide scavenging activity can be a useful indicator of anti-inflammatory activity. Nitric oxide (NO) is a short-lived free radical and intercellular messenger produced by various mammalian cells, such as macrophages, neutrophils, platelets, fibroblasts, endothelial cells, neurons, and smooth muscle cells. NO mediates a variety of biological events, including vasodilation, neurotransmission, platelet adhesion and aggregation inhibition, and is also involved in a wide range of inflammatory pathologies. The scavenging action against nitric oxide was determined using the Griess method, commonly used to detect the presence of nitrites and measure their concentration spectrophotometrically.
NITRIC OXIDE SCAVENGING ACTIVITY – ANTI-INFLAMMATORY ACTION
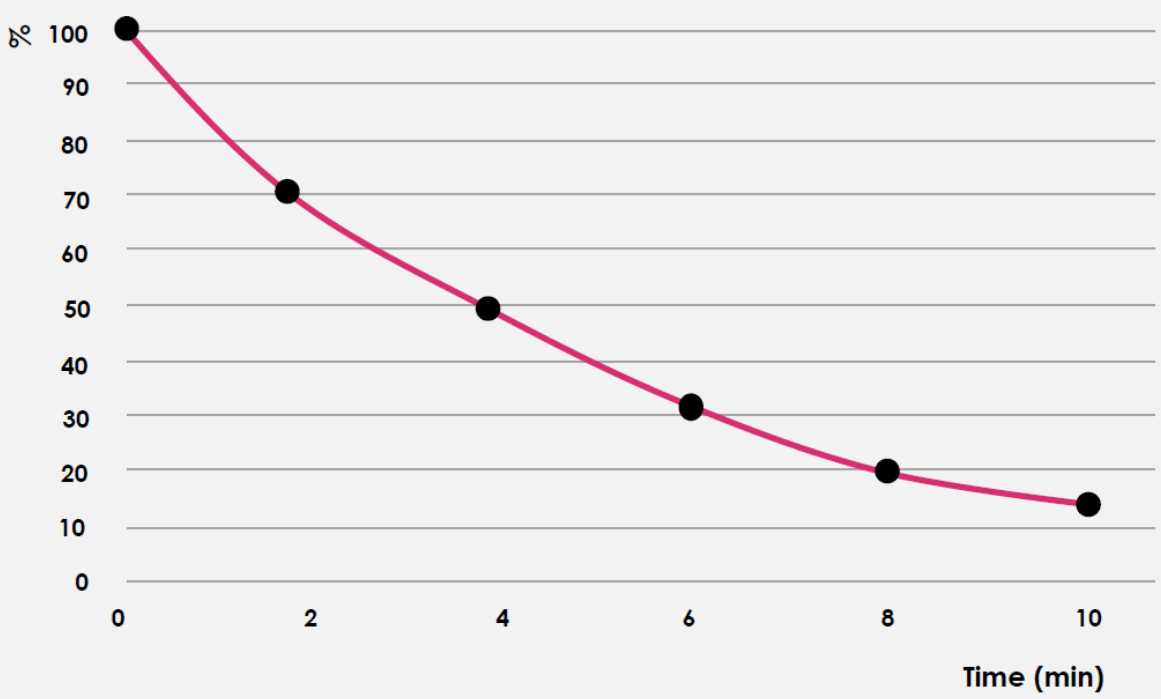
The data obtained from the conducted studies demonstrated the ability of ACTIVE-CO to reduce the inflammatory response, with an IC50 value of 25 mg/ml, indicating the concentration required to achieve 50% inhibition of the radical. This confirms the anti-inflammatory potential of the raw material.
Safety Assessment
IN VITRO ANALYSIS OF PRO-SENSITIZING POTENTIAL – SENSITIZATION TEST
The purpose of this test is to evaluate the absence of pro-sensitizing effects of finished cosmetic products or raw materials. In determining the cutaneous tolerability, it is important to consider not only the potential for irritation but also the potential sensitization of products and topical ingredients for safety purposes.
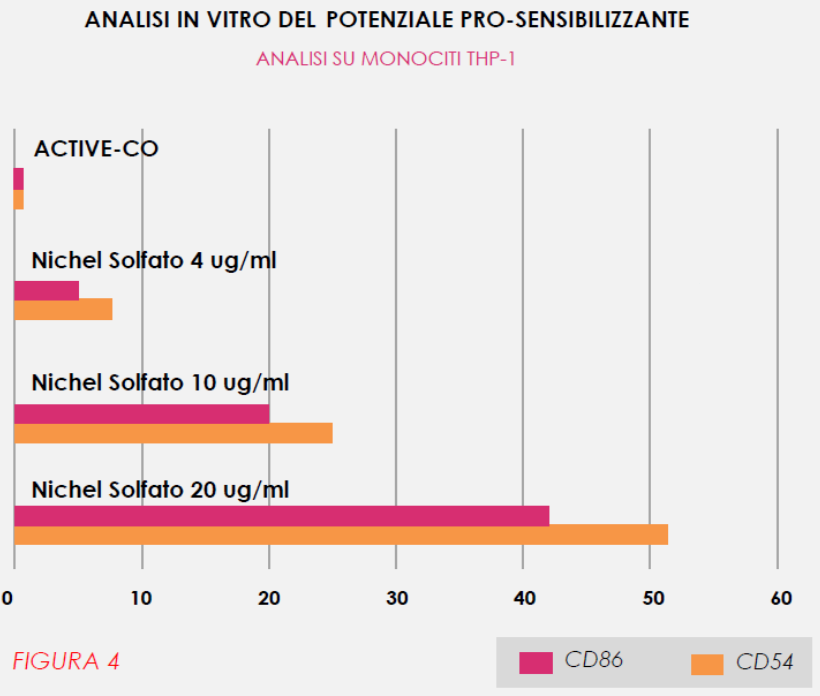
The test was performed on a monocyte cell line called THP-1, as this cell type is highly involved in immune responses of the skin, a typical target organ for topical products. The modulation of the expression of two co-stimulatory molecules, CD54 and CD86, was evaluated on these cells, using Nickel Sulfate as a positive control, a typical contact sensitizing substance.
Figure 4 shows the results of the analysis of the THP-1 monocyte cell line for the expression of co-stimulatory molecules by flow cytometry after 24 hours of reaction with the tested sample and controls, corrected for the negative control.
Under the experimental conditions adopted, the analyzed sample did not show any modulation of the investigated markers in human monocytes, indicating that it does not possess a stimulatory potential on the immune system mediated by monocytes/macrophages.