vegetable oils and butters
Vegetable oils obtained through cold pressing, characterized by a high content of bioactive compounds that provide anti-aging, moisturizing, and anti-inflammatory properties.
They can be used for various purposes in the formulation of cosmetic products with different qualities and characteristics.
This category also includes butters, which are solid at room temperature and are also widely used as ingredients in cosmetic products.
With vegetable oils, we have a certain variety of choices, which can be tailored according to the skin’s needs and the product formulation.
Applications:
- Moisturizing and emollient for skin care products
- Moisturizing and emollient for hair care products
- Moisturizing and emollient for pet care products
BAOBAB OIL
INCI: Adansonia Digitata Seed Oil
Baobab oil is a vegetable oil with soothing and protective properties, obtained through cold pressing of the inner endocarp of Baobab seeds. It is rich in essential fatty acids such as oleic acid, linoleic acid, and linolenic acid. It has soothing and anti-inflammatory properties that help alleviate skin irritation.
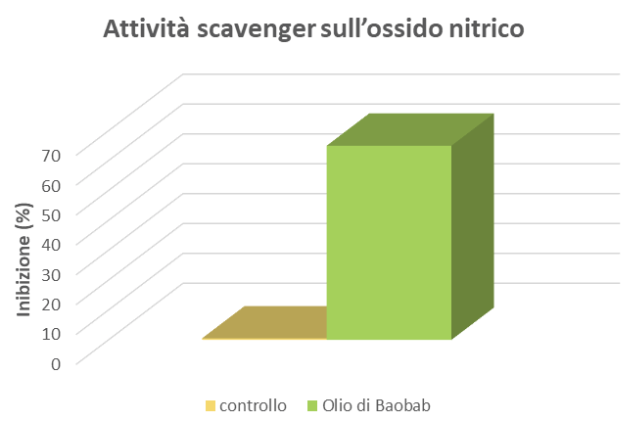
PROTECTIVE ACTION AGAINST INFLAMMATION – Nitric Oxide Scavenging Activity
In vitro determination of nitric oxide scavenging activity can be a useful indicator of anti-inflammatory activity. Nitric oxide (NO) is a short-lived free radical and intercellular messenger produced by a variety of mammalian cells, such as macrophages, neutrophils, platelets, fibroblasts, endothelial cells, neuronal cells, and smooth muscle cells. NO mediates a variety of biological events, ranging from vasodilation, neurotransmission, inhibition of platelet adhesion and aggregation, and is also involved in a wide range of inflammatory conditions.
The scavenging action against nitric oxide was determined using the Griess method.
The reaction is conducted using the Griess reagent, which is a mixture of sulfanilamide and 1-naphthylethylenediamine in an acidic environment. Under these conditions, nitrite tends to form nitrous acid, which reacts with sulfanilamide to produce a diazonium salt (diazotization reaction).
The diazonium salt then undergoes a coupling reaction with 1-naphthylethylenediamine, forming a purple azo dye with a maximum absorption peak at a wavelength of 540 nm.
The obtained data demonstrated the ability of Baobab Oil to inhibit the radical.
BURITI OIL
INCI: Mauritia Flexuosa Fruit Oil
CAS: 394239-67-9; 906350-92-3
Buriti oil is a vegetable oil obtained through cold pressing of the fruits of Mauritia Flexuosa, a plant belonging to the Arecaceae family, native to the Amazon rainforest. Buriti oil has a high emollient and antioxidant power due to its high content of fatty acids and carotenoids, known for their antioxidant properties.
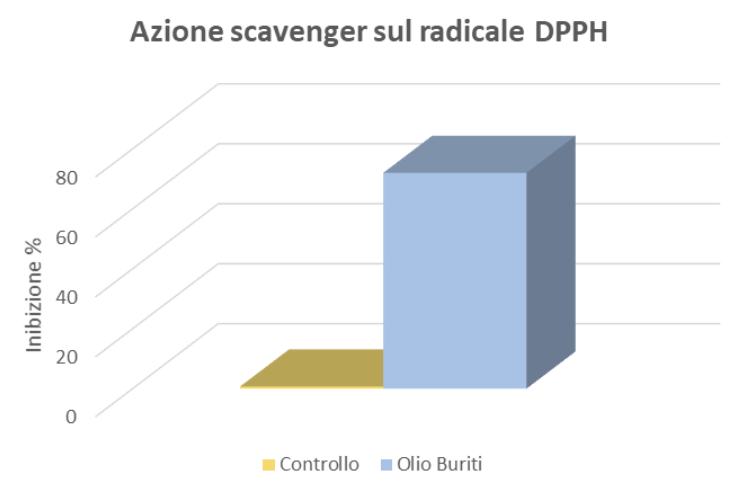
Evaluation of Antioxidant Activity: DPPH Radical Scavenging Action
DPPH (2,2′-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl) is an organic free radical with a maximum absorption peak at 515-528 nm, allowing the antioxidant activity of various compounds to be evaluated using spectrophotometric measurements.
The reaction involves the reduction of the DPPH radical by antioxidant molecules, forming a yellow compound, diphenylpicrylhydrazine. The extent of the reduction reaction depends on the ability of the molecules to act as electron donors.
To evaluate the antioxidant properties of the product under examination, the scavenging activity against DPPH radicals was determined by adding HydraOIL to 9.9 ml of a DPPH solution (200 µM) prepared in ethanol. The absorbance was read after 15 minutes at 517 nm.
The data were expressed as a percentage of inhibition and are shown in the figure.
CHIA OIL
INCI: Salvia Hispanica Seed Oil
CAS: 93384-40-8
EC: 297-250-8
Chia oil is a vegetable oil obtained through cold pressing of chia seeds (Salvia Hispanica), ideal as an active ingredient in skin and hair treatments. It is rich in essential fatty acids, phytosterols, and vitamin E with antioxidant properties.
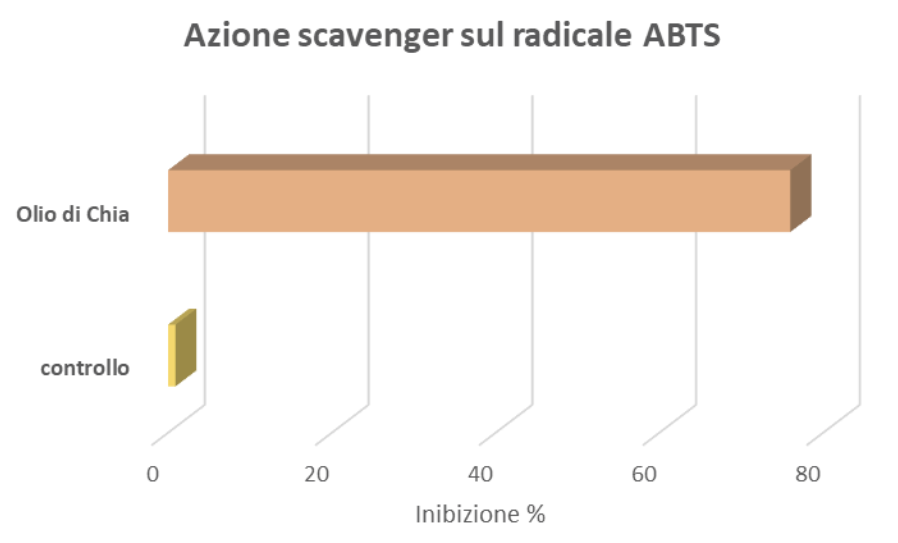
Evaluation of Antioxidant Activity: ABTS Radical Scavenging Action
BTS (2,2′-azinobis-(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid)) is a hydrophilic radical with a maximum absorption around 734 nm. The reaction depends on the ability of the antioxidant to donate hydrogen atoms.
The method is based on the ability of antioxidants to act on the ABTS radical cation, a blue-green chromophore with characteristic absorption at 734 nm. ABTS•+ was generated by reacting an aqueous solution of ABTS (7 mM) with potassium persulfate (2.45 mM, K2S2O8). The mixture was kept in the dark at room temperature and, after 16 hours, diluted with distilled water to an absorbance of 0.999 ± 0.030 at 734 nm.
To evaluate the antioxidant properties, Chia Oil was added to 1 ml of the final ABTS solution and 0.9 ml of distilled water.
A control was prepared under the same reaction conditions using distilled water instead of the sample. After 6 minutes, the absorbance was measured at 734 nm. The data obtained, expressed as a percentage of radical inhibition and shown in Figure 1, highlighted Chia Oil’s ability to inhibit the radical.
CHUFA OIL
INCI: Cyperus Esculentus Root Oil
CAS: 223748-92-3
EC: –
Chufa oil is a vegetable oil obtained through cold pressing of the root of Cyperus Esculentus, known for its moisturizing and antioxidant properties.
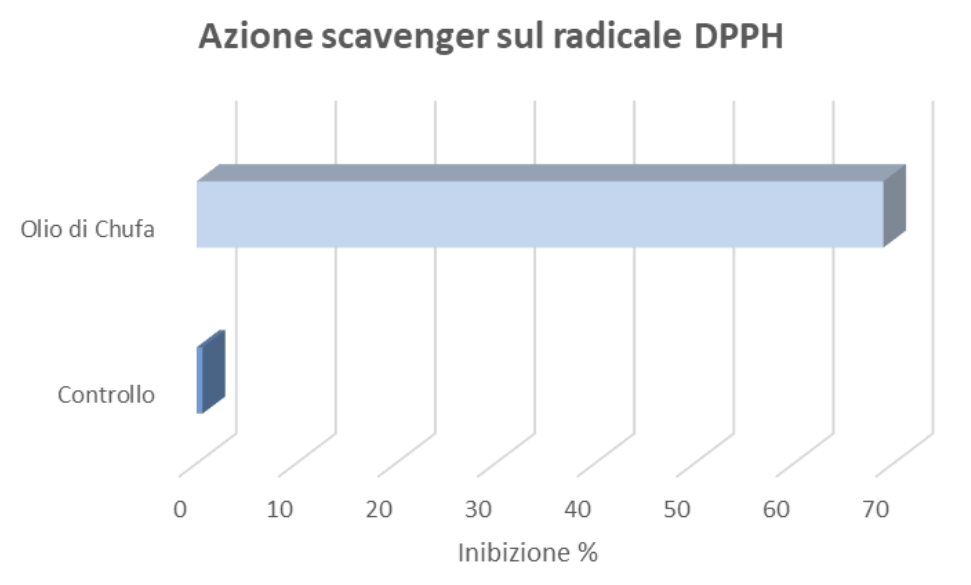
Evaluation of Antioxidant Activity: DPPH Radical Scavenging Action
DPPH (2,2’-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl) is an organic free radical with a maximum absorption peak at 515-528 nm, used to evaluate the antioxidant activity of various compounds through spectrophotometric measurements.
The reaction involves the reduction of the DPPH radical by antioxidant molecules, forming a yellow compound, diphenylpicrylhydrazine. The extent of the reduction reaction depends on the ability of the molecules to act as electron donors.
To evaluate the antioxidant properties of the product in question, the scavenging activity against DPPH radicals was determined by adding HydraOIL to 9.9 ml of a DPPH solution (200 µM) prepared in ethanol. The absorbance was read after 15 minutes at 517 nm.
The data were expressed as a percentage of inhibition and are shown in the figure.
SACHA INCHI OIL
INCI: Plukenetia Volubilis Seed Oil
CAS: –
EC: –
Sacha Inchi oil is a vegetable oil obtained through cold pressing of the seeds of the Plukenetia volubilis plant.
This oil is known for being rich in omega-3, omega-6, and omega-9 fatty acids, as well as antioxidants like vitamin E, making it valuable for skin care. It has notable anti-inflammatory properties.
Protective Action Against Inflammation: Nitric Oxide Scavenging Activity
In vitro determination of nitric oxide scavenging activity can be a useful indicator of anti-inflammatory activity. Nitric oxide (NO) is a short-lived free radical and intercellular messenger produced by a variety of mammalian cells, such as macrophages, neutrophils, platelets, fibroblasts, endothelial cells, neuronal cells, and smooth muscle cells.
NO mediates various biological events, including vasodilation, neurotransmission, inhibition of platelet adhesion and aggregation, and is involved in a wide range of inflammatory conditions.
The scavenging action against nitric oxide was determined using the Griess method. The reaction is conducted using the Griess reagent, which is a mixture of sulfanilamide and 1-naphthylethylenediamine in an acidic environment. Under these conditions, nitrite tends to form nitrous acid, which reacts with sulfanilamide to produce a diazonium salt (diazotization reaction).
The diazonium salt then undergoes a coupling reaction with 1-naphthylethylenediamine, forming a purple azo dye with a maximum absorption peak at a wavelength of 540 nm.
The obtained data demonstrated the ability of Sacha Inchi Oil to inhibit the radical.
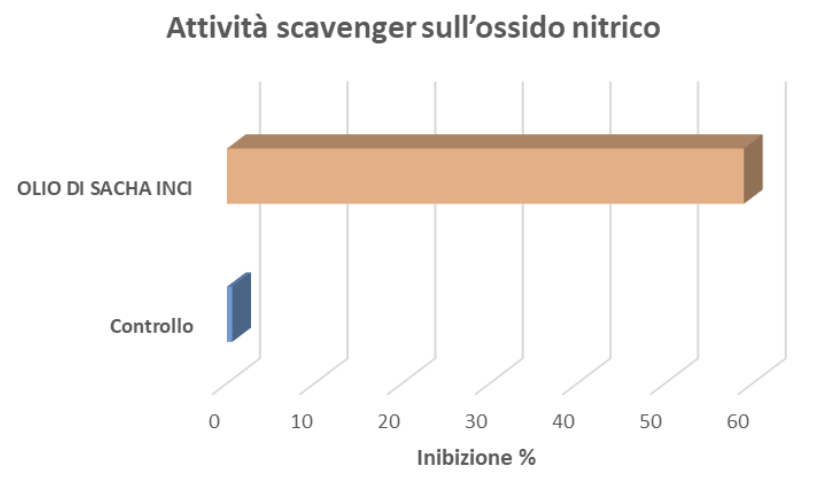
Foto: Forest & Kim StarrTAMANU OIL
INCI: Calophyllum Inophyllum Seed oil
CAS: –
EC: –
Tamanu oil is a vegetable oil obtained through cold pressing of the seeds of the Calophyllum inophyllum tree. This oil is rich in essential fatty acids and has healing, regenerating, and anti-inflammatory properties.
Determination of Regenerating Action: Wound Healing Assay
Cell migration is an important step in wound healing. For biological studies on cell migration, the Wound-Healing Scratch Assay method was used.
This assay is based on the observation that if an artificial gap called a “scratch” is created on confluent monolayer cells to simulate a wound, the cells along the edges of the scratch tend to move across the empty space until it is closed, re-establishing cell-to-cell contacts. The assay is intended to evaluate the sample’s ability to promote cell regeneration and thus contribute to the wound healing process.
Studies were conducted on a human fibroblast cell line treated with the sample for 24 hours.
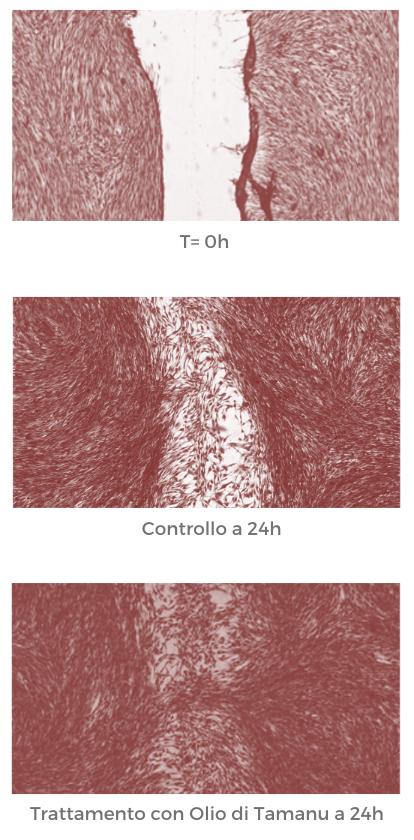
Foto: SvnavareKARANJA OIL
INCI: Pongamia Glabra Seed Oil
CAS: –
EC: –
Karanja oil is a vegetable oil obtained through cold pressing of the seeds of the Pongamia pinnata tree. Rich in oleic acid and linoleic acid, this oil has antioxidant properties and provides protection against UV rays.
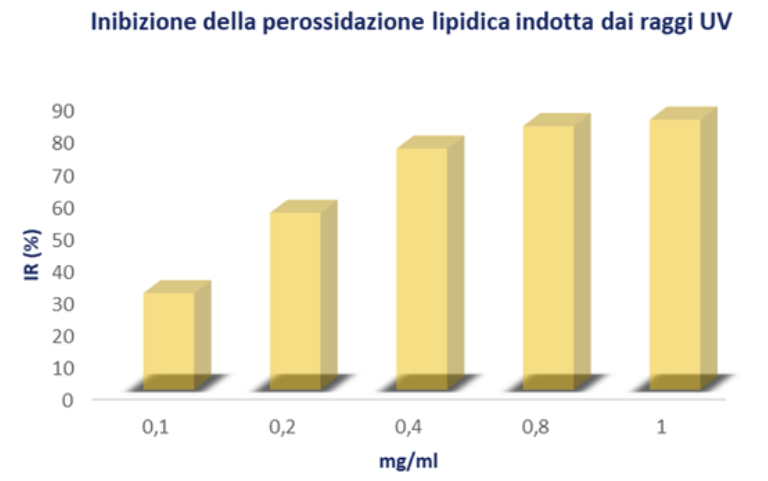
Inhibition of UV-Induced Lipid Peroxidation
UV radiation is a significant factor in generating oxidative stress. UV radiation can increase free radicals, leading to lipid peroxidation.
The inhibitory effect of Karanja oil on UV-induced lipid peroxidation was determined using the thiobarbituric acid method with some modifications.
A mixture containing 1 ml of 10 mg/ml lecithin (dissolved in PBS, 10 mM pH 7.4) and 1 ml of various concentrations of Karanja Oil was exposed to UVC for 30 minutes after 30 minutes of incubation at 37°C. Subsequently, 2 ml of TCA-TBA-HCl mixture (15% TCA, 0.4% TBA, 2% HCl) was added and brought to a boil for 15 minutes.
After cooling in ice water, the tubes were centrifuged at 1000 rpm for 10 minutes, and the absorbance of the supernatant was measured at 535 nm using a spectrophotometer. The Resistance Index (RI), or the ability to resist peroxidation, was calculated as follows:
where ODn is the absorbance of the control, and ODs is the absorbance of the sample reaction solution.
The data obtained from the conducted studies demonstrated the ability of Karanja Oil to inhibit UV-induced lipid peroxidation.
CHAULMOOGRA OIL
INCI: Taraktogenos Kurzii Seed Oil
CAS: 8001-74-9
EC: 616-787-4
Chaulmoogra oil is a vegetable oil with moisturizing and emollient properties, obtained through cold pressing of the seeds of Taraktogenos kurzii. It has excellent anti-inflammatory and lipolytic properties.
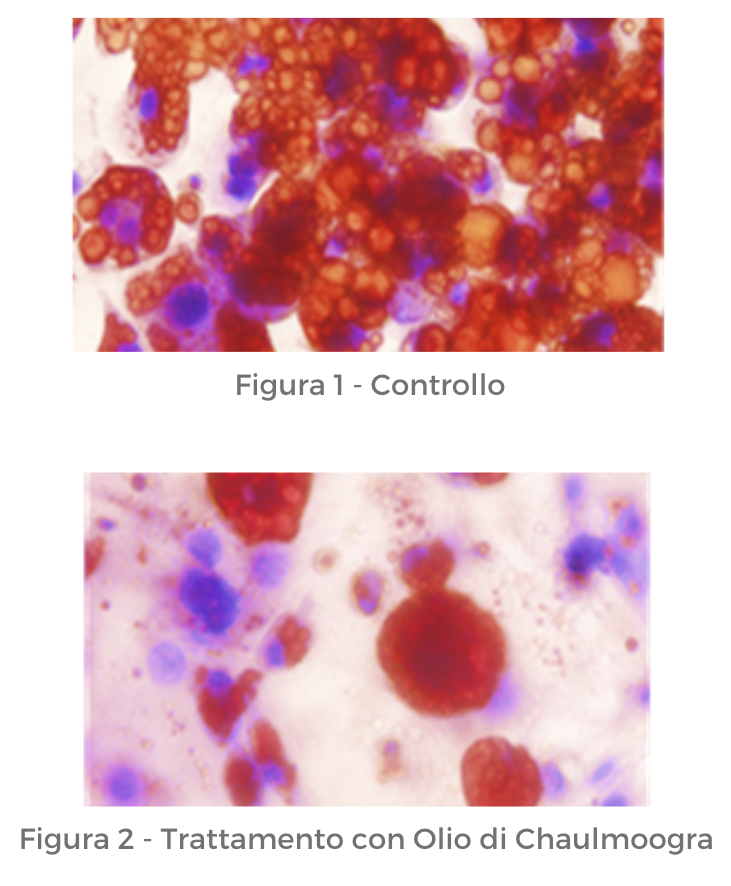
Evaluation of Liporeducing/Anti-Cellulite Activity – Oil Red O Staining Protocol
The in vitro biological evaluation of lipid granules was determined using the Oil Red O Assay performed on 3T3-L1 cells.
The results, shown in the figure, demonstrated the ability of Chaulmoogra oil to reduce intracellular lipid content in 3T3-L1 adipocytes.
MARULA OIL
INCI: Sclerocarya Birrea Seed Oil
CAS: 8001-74-9
EC: 616-787-4
Marula oil is a vegetable oil with moisturizing and emollient properties, obtained through cold pressing of the seeds of Sclerocarya birrea. It has excellent moisturizing and anti-inflammatory properties and is also effective in slowing down hair loss.
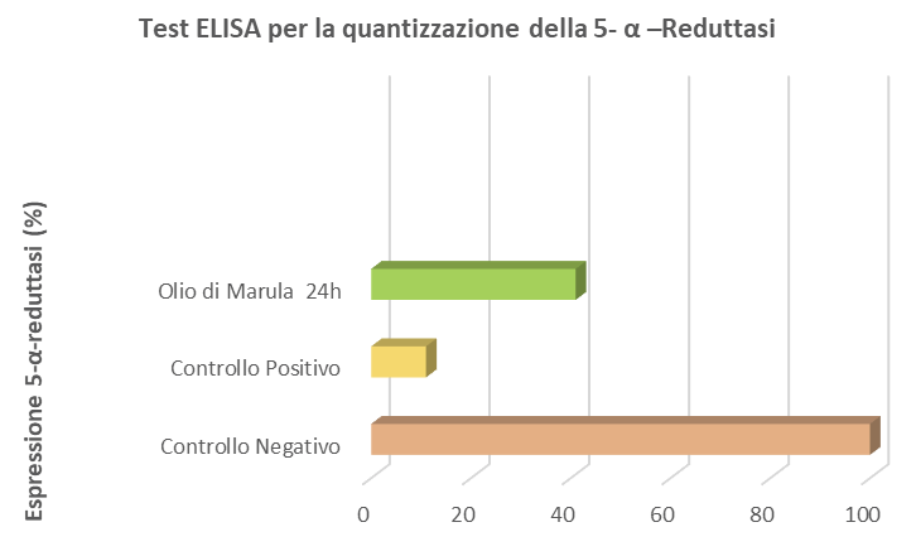
Determination of 5-α-Reductase Inhibition – ELISA Test for Quantifying 5-α-Reductase
To determine this, an indirect ELISA protocol was performed for the identification of 5-α-reductase in the culture medium of treated HHDPCs (Human Hair Dermal Papilla Cells).
Based on cell viability results, a sample concentration of 4 mg/ml was used for this test. A control sample was prepared by replacing the sample volume with an equal volume of culture medium.
Finasteride was used as a positive control. The results are shown in the figure.
Cells treated with Marula oil at the tested concentration and time points showed a reduction in the expression of the enzyme 5-α-reductase, with approximately a 40% reduction in levels recorded at 24 hours post-treatment compared to the control.
list of vegetable oils and butters
VEGETABLE OILS AND BUTTERS
|
ORGANIC VEGETABLES OILS
|
FUNCTIONALS OILS
|
